f you work in the architecture, engineering, or construction industry, you may have heard of BIM, or Building Information Modeling. BIM is a digital representation of a building’s physical and functional characteristics, including its geometry, spatial relationships, and building components. It is a powerful tool that assists in the design, construction, and operation of buildings.
BIM is a process that involves the generation and management of digital models of buildings. These models are created using specialized software that allows architects, engineers, and contractors to collaborate on building design and construction. BIM models can be used to simulate the building’s performance, analyze its energy efficiency, and identify potential problems before construction begins. They can also be used to manage the building’s maintenance and operation after it is completed. BIM is quickly becoming the industry standard for building design and construction, and many companies are adopting it as a way to improve their workflows and increase efficiency.
Understanding BIM
If you are new to the world of architecture, engineering, and construction, you may have heard the term BIM thrown around quite a bit. In this section, we will take a closer look at BIM, its history, and how it relates to CAD and VDC (Virtual Design and Construction).
History of BIM
BIM has been around since the 1970s, but it was not until the 1990s that it began to gain popularity. Chuck Eastman, a professor at Georgia Tech, is often credited with developing the first BIM software. Since then, BIM has become an essential tool in the AEC (Architecture, Engineering, and Construction) industry, allowing for more efficient and collaborative planning, design, and construction of buildings.
BIM and CAD
BIM and CAD (Computer-Aided Design) are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same thing. While CAD is primarily a 2D drafting tool, BIM is a 3D modeling tool that includes data and information about the building components. BIM takes the design process a step further by allowing architects, engineers, and contractors to collaborate in real-time and make changes to the model as needed.
BIM software also has the ability to simulate the building process, allowing for better planning and scheduling. It is also used to detect clashes between components, reducing the likelihood of errors during construction.
BIM is a valuable tool for the AEC industry, allowing for more efficient and collaborative planning, design, and construction of buildings. Its history dates back to the 1970s, and it has become an essential tool in the industry since then. While often confused with CAD, BIM is a 3D modeling tool that includes data and information about the building components, allowing for real-time collaboration and simulation of the building process.
Components of BIM
Building Information Modeling is a process that involves creating and managing information for a built asset. It is a holistic approach that encompasses different components, including BIM software, BIM objects, Common Data Environment (CDE), and Industry Foundation Classes (IFC).
BIM Software
BIM software is an essential component of the BIM process. It is a tool that helps you create and manage a 3D model of a building or infrastructure project. Some of the most popular BIM software tools include Autodesk Revit, AutoCAD, and Graphisoft.
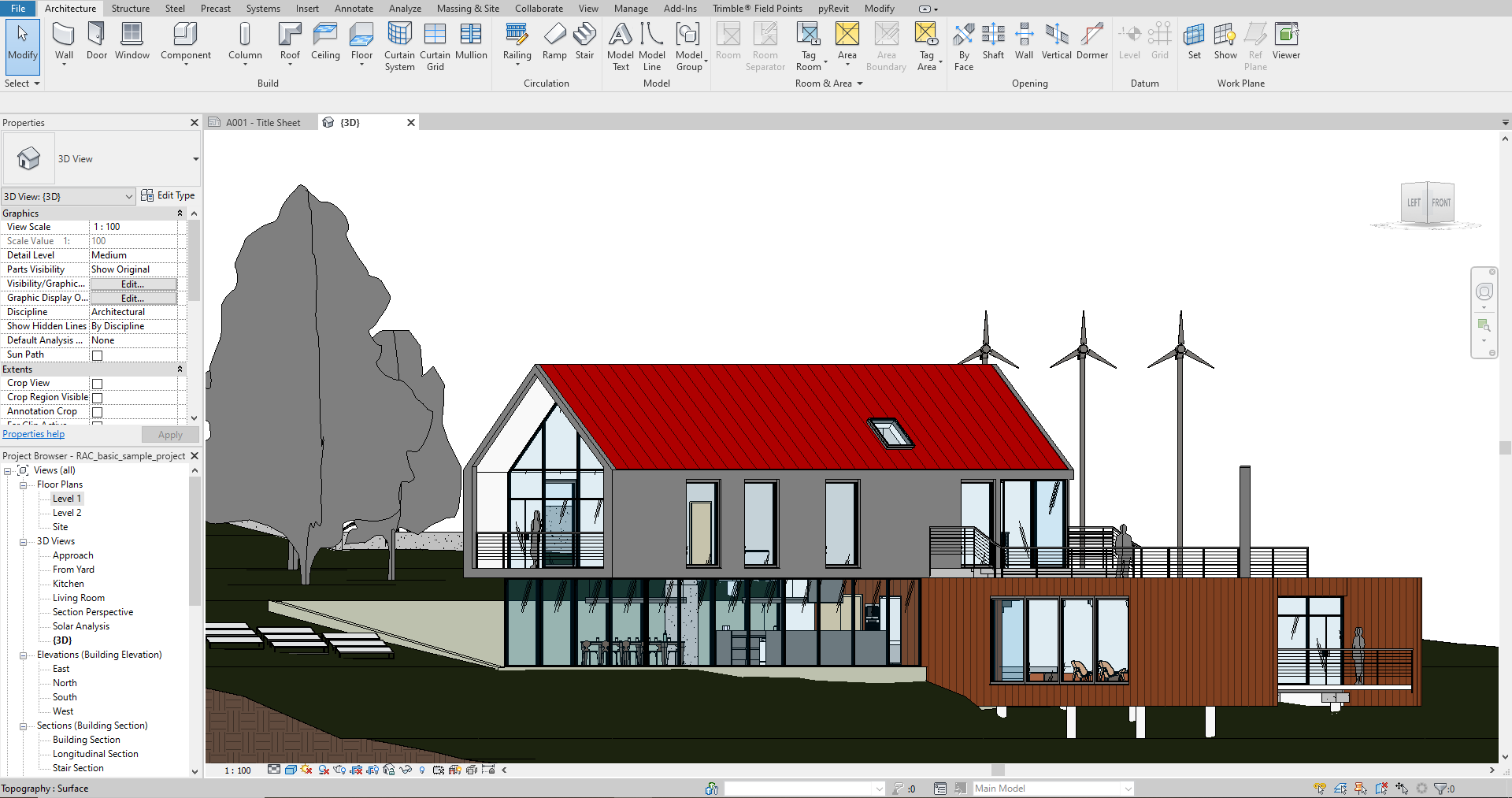
These tools allow you to create a 3D model of a building or infrastructure project, which can be used to visualize the project and identify potential issues before construction begins. BIM software also allows you to create 2D drawings from the 3D model, which can be used for construction documents.
BIM Objects
BIM objects are digital representations of building products and components that can be used in BIM software. They contain information about the product, such as its dimensions, material, and performance characteristics.
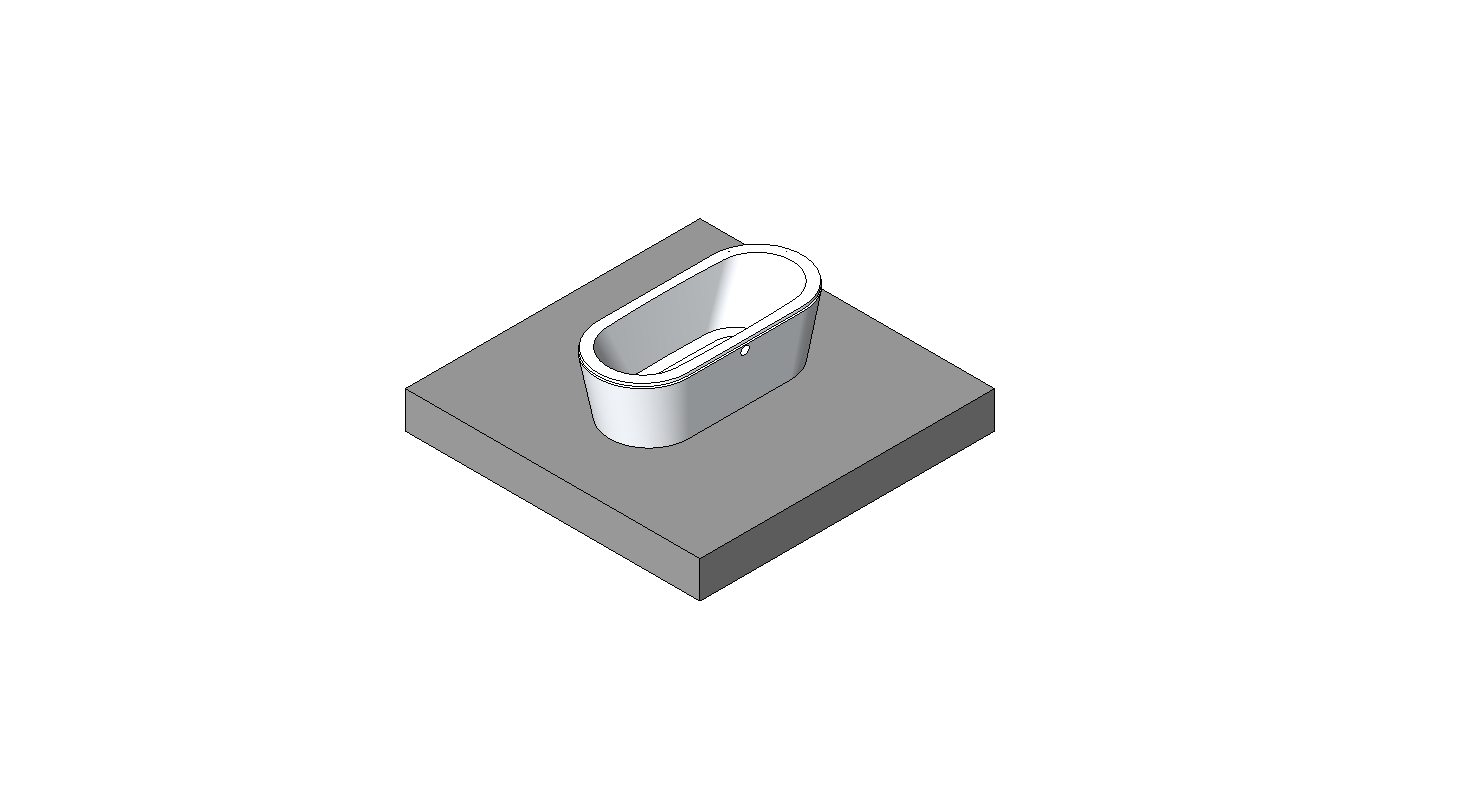
BIM objects can be downloaded from manufacturers’ websites or from online libraries such as BIMobject or NBS National BIM Library. Using BIM objects in your project can save time and improve accuracy, as the objects already contain all the necessary information.
Common Data Environment
A Common Data Environment (CDE) is a central location where all project information is stored and managed. It is a shared platform where all project stakeholders can access the latest project information, such as drawings, schedules, and specifications.
The CDE helps to improve collaboration and communication between project stakeholders, as everyone is working from the same information. It also helps to reduce errors and rework, as everyone is working from the latest information.
Industry Foundation Classes
Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) is a file format that is used to exchange data between different BIM software tools. It is an open standard that allows interoperability between different software tools, regardless of the software vendor.
IFC files contain information about the building or infrastructure project, such as its geometry, materials, and performance characteristics. They can be used to exchange information between different BIM software tools, ensuring that everyone is working from the same information.
BIM is a holistic approach to creating and managing information for a built asset. Its components, including BIM software, BIM objects, Common Data Environment, and Industry Foundation Classes, are essential to the BIM process. By using these components, you can improve collaboration, reduce errors, and improve the overall efficiency of your project.
BIM in Design and Construction
In the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry, Building Information Modeling involves the creation and management of digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of buildings. BIM is a powerful tool that can be used throughout the entire lifecycle of a construction project, from planning and design to construction and maintenance.
Planning with BIM
BIM is an essential tool for planning a construction project. By using BIM, architects and construction managers can create accurate and detailed 3D models of the building design. This helps you to identify potential issues and conflicts in the design before construction begins, which can save you time and money in the long run. BIM also allows you to create detailed construction schedules and manage the project more efficiently.
Construction with BIM
During the construction phase of a project, BIM can help you to manage the construction process more effectively. BIM can be used to create detailed construction drawings and models, which can be used to guide construction workers and ensure that the construction is completed according to the design specifications. BIM can also be used to manage construction schedules and monitor progress, allowing you to identify potential delays or issues and take corrective action.
Visualization and Communication
BIM is a powerful tool for visualization and communication. By using BIM, you can create detailed 3D models of the building design, which can be used to visualize the design and communicate it to stakeholders. BIM can also be used to create virtual walkthroughs of the building design, allowing stakeholders to experience the design in a more immersive way. BIM can also be used to create detailed construction documentation, which can be used to communicate design specifications and requirements to contractors and construction workers.
By using BIM, you can create accurate and detailed 3D models of the building design, manage construction schedules more effectively, and communicate design specifications and requirements more clearly to stakeholders.
Role of BIM in Project Management
BIM plays a crucial role in project management by providing a comprehensive 3D model of the building design. This model can be used by the project team to collaborate and coordinate effectively, detect clashes, and manage change orders efficiently. In this section, we will explore the different ways in which BIM impacts project management, including collaboration and coordination, clash detection, and change orders.
Collaboration and Coordination
BIM facilitates collaboration and coordination between the project team members, including architects, engineers, contractors, and subcontractors. With BIM, you can share the 3D model with all the stakeholders, allowing them to visualize the design and identify potential issues before construction begins. This helps to reduce errors and rework, resulting in cost savings and improved project outcomes.
Moreover, BIM enables the project team to work together in real-time, regardless of their location, using cloud-based tools. This means that you can access the latest version of the model and collaborate with other team members, even if you are not physically present on the site. This improves communication and reduces delays, ensuring that the project stays on schedule.
Clash Detection
BIM also helps to detect clashes between different building systems, such as mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems. With BIM, you can overlay the different systems on top of each other and identify any conflicts or clashes. This allows you to resolve these issues before construction begins, reducing the risk of delays, rework, and cost overruns.
Using BIM for clash detection also helps to improve safety on the construction site. By identifying clashes early on, you can ensure that the different building systems are installed correctly and in compliance with safety regulations.
Change Orders
BIM also facilitates the management of change orders, which are a common occurrence in construction projects. With BIM, you can quickly and easily update the 3D model to reflect any changes in the design. This allows you to visualize the impact of the change on the entire project and make informed decisions about whether to approve or reject the change order.
Using BIM for change orders also helps to reduce the risk of errors and miscommunications. By having a centralized 3D model, all the stakeholders can see the same information, reducing the risk of misunderstandings and mistakes.
BIM plays a critical role in project management by facilitating collaboration and coordination, clash detection, and change order management. By leveraging the power of BIM, you can improve project outcomes, reduce costs, and ensure that your project stays on schedule.
BIM and Building Lifecycle
BIM has revolutionized the way buildings are designed, constructed, and operated. BIM involves creating a digital model that contains all the information about a building, including its physical and functional characteristics. This model is used throughout the building’s lifecycle, from planning and design to construction, operations, and maintenance.
Operations and Maintenance
BIM has transformed the way buildings are operated and maintained. With BIM, all the information about a building is stored in a digital model, making it easy to access and manage. This information includes details about the building’s systems, equipment, and components, as well as maintenance schedules and procedures. BIM also allows for the tracking of building performance, making it possible to identify issues and optimize building operations.
Sustainability and Efficiency
BIM has also had a significant impact on building sustainability and efficiency. By using BIM, architects and engineers can model and analyze a building’s energy performance, helping to identify opportunities to reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. BIM can also be used to optimize building systems and equipment, improving efficiency and reducing operating costs.
In addition, BIM can help to minimize waste during construction and reduce the environmental impact of buildings. By modeling and analyzing the building’s materials and construction processes, architects and contractors can identify opportunities to reduce waste and minimize the use of non-renewable resources.
BIM has transformed the way buildings are designed, constructed, and operated. By using BIM, building owners, architects, engineers, and contractors can work together to create more sustainable, efficient, and cost-effective buildings.
BIM Standards and Regulations
BIM Standards and Regulations are essential to ensure that all parties involved in the construction and lifecycle management of built assets work collaboratively and share data effectively. In this section, we will discuss two essential BIM standards: ISO 19650 and COBie Standard.
ISO 19650
ISO 19650 is an international standard for managing information over the whole life cycle of a built asset using Building Information Modelling (BIM). It contains all the same principles and high-level requirements as the UK BIM Framework and is closely aligned with the current UK 1192 standards.
The ISO 19650 standard provides guidelines for the implementation of BIM, including the exchange of information, the use of data, and the creation of models. It is an essential standard for BIM professionals, architects, engineers, and contractors who want to collaborate and share information effectively.
COBie Standard
COBie (Construction Operations Building Information Exchange) is a standard for the exchange of information between different parties involved in the construction process. It provides a common language for sharing information about the built environment, including building components, equipment, and systems.
COBie is an open standard that is designed to be used with BIM, and it is widely used in the United Kingdom and the United States. It allows for the exchange of data in a structured format, making it easier for all parties to understand and use the information.
COBie is a valuable tool for BIM professionals, as it ensures that all parties have access to the same information, reducing errors and improving communication. It is also useful for facility managers who need access to accurate information about the building’s components and systems.
BIM standards and regulations are essential for the effective implementation of BIM. ISO 19650 and COBie are two crucial standards that provide guidelines for the exchange of information and the use of data. By following these standards, you can ensure that all parties involved in the construction process work collaboratively and share data effectively.
The Future of BIM
As BIM technology continues to evolve, the future of BIM is looking increasingly promising. Here are some of the emerging technologies and trends that will shape the future of BIM:
Emerging Technologies
One of the most exciting trends in BIM technology is the use of virtual and augmented reality. These technologies allow AEC professionals to visualize and interact with their designs in a more immersive way, making it easier to identify potential issues and make changes before construction begins. Another emerging technology is the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate certain aspects of the design process, such as generating building layouts or optimizing energy efficiency.
BIM and AEC Professionals
As BIM technology becomes more widespread, AEC professionals will need to adapt to new ways of working. This means developing new skills and expertise in areas such as data management, automation, and virtual reality. It also means collaborating more closely with other professionals, such as engineers and contractors, to ensure that everyone is working towards the same goals.
In addition, BIM technology will continue to drive development in the AEC industry. For example, the use of BIM can help reduce waste and improve efficiency, leading to more sustainable and cost-effective building practices.
The future of BIM is bright, with exciting new technologies and trends on the horizon. As an AEC professional, it is important to stay up-to-date with these developments and continue to develop your skills and expertise in this area.
Benefits of BIM
BIM technology offers several benefits to various stakeholders involved in the construction industry. However, implementing BIM also comes with its own set of challenges. Here are some of the benefits of BIM:
Increased Productivity
BIM technology enables you to create a 3D model of a building that can be used to visualize and simulate the construction process. This helps to identify and resolve issues early on, reducing the likelihood of errors and rework. As a result, you can complete projects faster and with greater efficiency.
Cost Estimation
BIM technology allows you to create a detailed model of a building that contains all the necessary information about its components and systems. This can be used to accurately estimate the cost of the project, including the cost of materials, labor, and equipment. This helps to reduce the likelihood of unexpected expenses and cost overruns.
Improved Decision-Making
BIM technology provides you with a comprehensive view of a project, enabling you to make informed decisions about design, construction, and maintenance. This helps to reduce the likelihood of errors and rework and ensures that the project is completed on time and within budget.
Improved Safety
BIM technology enables you to identify and address potential safety hazards early on, reducing the likelihood of accidents and injuries on the construction site. This helps to create a safer working environment for everyone involved in the project.
Challenges of BIM
Although BIM technology offers several benefits to the construction industry, it also poses its own set of challenges. Let’s explore these challenges:
Implementation Cost
Implementing BIM technology can be expensive, requiring significant investment in hardware, software, and training. This can be a barrier to adoption for some companies, particularly smaller ones.
Resistance to Change
Implementing BIM technology requires a significant change in the way that you work. This can be challenging for some employees, who may be resistant to change or struggle to adapt to new technologies.
Data Management
BIM technology generates a large amount of data, which can be difficult to manage and organize effectively. This can lead to confusion and errors if not managed properly.
Collaboration
BIM technology requires collaboration between various stakeholders, including engineers, contractors, and owners. This can be challenging if there is a lack of communication or if stakeholders have different goals or priorities.
BIM technology offers several benefits to the construction industry, including increased productivity, cost estimation, improved decision-making, and improved safety. However, implementing BIM also comes with its own set of challenges, including implementation cost, resistance to change, data management, and collaboration.
BIM Case Studies
BIM has been implemented in various projects across different sectors, including individuals, businesses, and government agencies. Here are some examples of BIM case studies:
Water and Gas Industry
In the water and gas industry, BIM has been used to improve the design and construction of infrastructure projects. For instance, the San Francisco Public Utilities Commission (SFPUC) used BIM for its $4.6 billion water system improvement program. The program involved upgrading the existing water system to ensure a reliable and sustainable water supply for the city. BIM was used to create a 3D model of the water system, which helped to identify and resolve design conflicts before construction began. As a result, the project was completed on time and within budget.
Ports
BIM has also been used in the port industry to improve the design and construction of port facilities. For example, the Port of Rotterdam used BIM to develop its new Maasvlakte 2 terminal. BIM was used to create a digital model of the terminal, which helped to optimize the design and construction process. The model was also used to simulate the terminal’s operations, which helped to identify potential bottlenecks and improve the terminal’s efficiency.
Government Agencies
Government agencies have also used BIM to improve the design and construction of public infrastructure projects. For instance, the UK government has mandated the use of BIM for all public sector projects since 2016. The mandate requires the use of BIM for all projects, regardless of their size or complexity. As a result, BIM has become an integral part of the UK’s construction industry, helping to improve the quality and efficiency of public infrastructure projects.
Businesses
Businesses have also adopted BIM to improve their construction projects. For example, Skanska, a multinational construction company, used BIM for its 30 St Mary Axe project in London. BIM was used to create a 3D model of the building, which helped to identify and resolve design conflicts before construction began. The model was also used to simulate the building’s operations, which helped to optimize the building’s energy efficiency.
Individuals
Individuals have also used BIM to improve their construction projects. For example, a homeowner in the UK used BIM to design and build a new home. BIM was used to create a 3D model of the home, which helped to optimize the design and construction process. The model was also used to simulate the home’s energy performance, which helped to identify potential energy savings.
These case studies demonstrate the benefits of BIM in improving the design and construction of infrastructure projects across different sectors.
Final Thoughts
BIM is a powerful tool that can revolutionize the way you approach construction projects. By creating a digital representation of every aspect of the built asset, BIM can help you make more informed decisions, reduce errors and omissions, and streamline the entire construction process.
If you’re new to BIM, there are plenty of resources available to help you get started. Check out our other articles for more details on BIM dimensions, applications, and benefits. You may also want to consider enrolling in a BIM training program or hiring a BIM consultant to help you navigate the complexities of this technology.
Remember, BIM is not a silver bullet that will solve all your construction problems overnight. It requires a significant investment of time, money, and effort to implement properly. However, if you’re willing to put in the work, BIM can help you achieve greater efficiency, accuracy, and profitability in your construction projects.
So, whether you’re a contractor, architect, engineer, or owner, BIM is worth considering as a valuable tool in your construction arsenal. With its ability to enhance collaboration, communication, and coordination, BIM can help you deliver better projects faster and more cost-effectively than ever before.
List of BIM Softwares: Top Tools for Building Information Modeling Professionals
Are you looking for the best BIM software to streamline your construction projects? Building Information Modeling (BIM) software enables architects, engineers, and construction professionals to create and manage digital models of buildings and infrastructure projects....
Related Articles
List of BIM Softwares: Top Tools for Building Information Modeling Professionals
Are you looking for the best BIM software to streamline your construction projects? Building Information Modeling (BIM) software enables architects, engineers, and construction professionals to create and manage digital models of buildings and infrastructure projects....